SWOT Analysis of a Nurse Residency Program Discussion
SWOT Analysis of a Nurse Residency Program Discussion
SWOT Analysis of a Nurse Residency Program Discussion
Conduct a SWOT analysis of an existing program with which you are familiar. This could be a program in your current setting, a program you have taught in as a faculty member, or a program you have taken as a learner.
Use the SWOT analysis to determine opportunities for program evaluation and revision. Consider how you can bolster strengths and eliminate weaknesses. In 250-500 words, identify the key findings of your SWOT analysis .
CLICK HERE TO ORDER YOUR ASSIGNMENT
In addition to conducting the SWOT analysis, design a concept map to show your next steps for program design. Your concept map should also include the resources, stakeholders, and relationships of the program’s outcomes to the program’s delivery, setting, and community.
Identify strategies for continuous quality improvement, with attention to professional and regulatory agency benchmarking for program performance SWOT Analysis of a Nurse Residency Program Discussion.
While APA style is not required for the body of this assignment, solid academic writing is expected, and documentation of sources should be presented using APA formatting guidelines, which can be found in the APA Style Guide, located in the Student Success Center.
SWOT Analysis Tool—Assignment 1—Part B
A SWOT analysis will help you identify internal and external factors in the environment that can help your practicum organization’s readiness for the implementation of your proposed project. At a minimum, identify four criteria for each of the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats elements. The presence of weaknesses and threats are gaps to be addressed in planning, while the absence of strengths or opportunities clarifies the need for further planning or development before implementation. After you have completed your analysis, write a 500 word summary of how this assessment will help you plan and manage your project. Include information from your weighted scoring model—part A.
The following two boxes are examples with possible suggestions. You can choose to use them or not:
| Internal Criteria Factor Examples: | External Criteria Factor Examples: |
| · Collective capabilities · Morale, commitment, leadership · Governance, participation norms, and defined roles · Resources, funding, assets, people· Experience, knowledge, data · Innovative aspects · Collaboration tools · Processes, systems, IT, and communications · Cultural, attitudinal, behavioral norms | · Political, legislative, and financial environment · Stakeholder involvement · Technology development and innovation· Development of knowledge · Uptake in disseminated knowledge or best practices |
| Factors to Maintain | Factors to Address | |
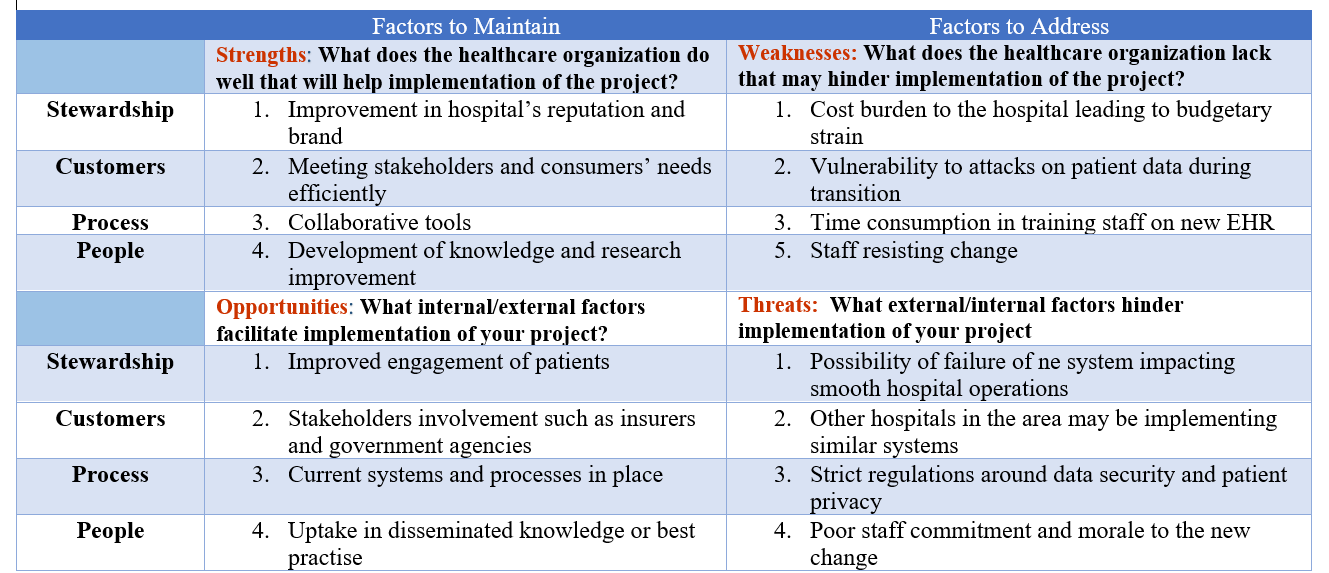
| Strengths: What does the healthcare organization do well that will help implementation of the project? | Weaknesses: What does the healthcare organization lack that may hinder implementation of the project? | |
| Stewardship | 1. Improvement in hospital’s reputation and brand | 1. Cost burden to the hospital leading to budgetary strain |
| Customers | 2. Meeting stakeholders and consumers’ needs efficiently | 2. Vulnerability to attacks on patient data during transition |
| Process | 3. Collaborative tools | 3. Time consumption in training staff on new EHR |
| People | 4. Development of knowledge and research improvement | 5. Staff resisting change |
| Opportunities: What internal/external factors facilitate implementation of your project? | Threats: What external/internal factors hinder implementation of your project | |
| Stewardship | 1. Improved engagement of patients | 1. Possibility of failure of ne system impacting smooth hospital operations |
| Customers | 2. Stakeholders involvement such as insurers and government agencies | 2. Other hospitals in the area may be implementing similar systems |
| Process | 3. Current systems and processes in place | 3. Strict regulations around data security and patient privacy |
| People | 4. Uptake in disseminated knowledge or best practise | 4. Poor staff commitment and morale to the new change |
| Summary:A healthcare organization has decided to improve patient care organization by reducing medication errors. There are various projects that health organizations would partake in to improve medication safety. Four selected feasible were transitioning to a new electronic health record (EHR) system, additional barcode medication administration technology, reverting to paper-based information systems, and using computerized physician order entry (CPOE). Many health organizations have implemented various evidence-based strategies to improve medication safety by reducing the risks of medication errors (Mutair et al., 2021). The health organization would consider various parameters to decide the best strategy. I conducted a Weighted Scoring Model for these projects to determine the best-fit project to improve patient medication safety. The weightage criteria used four parameters: estimated cost, staff training requirements, data security, patient engagement, and overall impact on hospital operations. The weightage for these parameters was based on the contemporary and online market values for specific strategies and not their actual values. These projects focused on improving information systems and interdisciplinary communication. By improving communication and documentation care transitions, medication reconciliations, and minimizing interruptions would be improved. According to Schepel et al. (2019), communication and collaboration improve involvement in patient care and system-based medication safety work. However, project costs, staff training requirements, data security, patient engagement, and overall impact on hospital operations were key issues that would determine the success of these projects. According to Flatman (2021), project sustainability and spread, appreciating interdisciplinary roles and improving the virtual work environment improve medication safety. The outcomes of the Weighted Scoring Model supported transitioning to the new EH system as the most suitable project to improve patient safety. Its weightage score was 69. Transitioning to a new EH system will require phasing out the pre-existing system and replacing it smoothly with a new EHR system with more advanced features ad patient involvement. This assignment would help me plan and manage the selected project in many ways. In this case, the SWOT analysis was used to plan the hospital’s transition to a new Electronic Health Record (EHR) system. When planning and managing a hospital project, SWOT analyses help me identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in both the internal and external environments. With the information gathered from the SWOT analysis, project managers can make informed decisions and take appropriate measures to mitigate risks, based on the priorities and potential risks associated with the project. Therefore, I will be able to plan effectively and be aware of pertinent risks that would come with making this project successful. To be able to assess the different EHR systems under consideration and determine which is the best fit for the hospital, I will need to use the Weighted Scoring Model. By analyzing the scores, I will gain valuable insight into how important each criterion really is, and can then prioritize my efforts during the implementation phase of the project based on these results. Therefore, the SWOT analysis and Weighted Scoring Model will be essential tools for managing and planning the EHR project. The SWOT analysis will provide a comprehensive analysis of the hospital’s internal and external environments, while the Weighted Scoring Model will provide a systematic and structured method for evaluating and comparing different EHR systems. |
SWOT Analysis of a Nurse Residency Program Discussion References
Flatman, J. (2021). How to improve medication safety at hospital discharge: let’s get practical. Future Healthcare Journal, 8(3), e616–e618. https://doi.org/10.7861/fhj.2021-0176
Mutair, A. A., Alhumaid, S., Shamsan, A., Zaidi, A. R. Z., Mohaini, M. A., Al Mutairi, A., Rabaan, A. A., Awad, M., & Al-Omari, A. (2021). The effective strategies to avoid medication errors and improving reporting systems. Medicines (Basel, Switzerland), 8(9), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines8090046
Schepel, L., Aronpuro, K., Kvarnström, K., Holmström, A.-R., Lehtonen, L., Lapatto-Reiniluoto, O., Laaksonen, R., Carlsson, K., & Airaksinen, M. (2019). Strategies for improving medication safety in hospitals: Evolution of clinical pharmacy services. Research in Social & Administrative Pharmacy: RSAP, 15(7), 873–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sapharm.2019.02.004
