NURS 6521 Week 3 EmmaGarcia Asthma and Stepwise Management
NURS 6521 Week 3 EmmaGarcia Asthma and Stepwise Management – Step-by-Step Guide
The first step before starting to write the NURS 6521 Week 3 EmmaGarcia Asthma and Stepwise Management, it is essential to understand the requirements of the assignment. The first step is to read the assignment prompt carefully to identify the topic, the length and format requirements. You should go through the rubric provided so that you can understand what is needed to score the maximum points for each part of the assignment.
It is also important to identify the audience of the paper and its purpose so that it can help you determine the tone and style to use throughout. You can then create a timeline to help you complete each stage of the paper, such as conducting research, writing the paper, and revising it to avoid last-minute stress before the deadline. After identifying the formatting style to be applied to the paper, such as APA, you should review its use, such as writing citations and referencing the resources used. You should also review how to format the title page and the headings in the paper.
How to Research and Prepare for NURS 6521 Week 3 EmmaGarcia Asthma and Stepwise Management
The next step in preparing for your paper is to conduct research and identify the best sources to use to support your arguments. Identify the list of keywords from your topic using different combinations. The first step is to visit the university library and search through its database using the important keywords related to your topic. You can also find books, peer-reviewed articles, and credible sources for your topic from PubMed, JSTOR, ScienceDirect, SpringerLink, and Google Scholar. Ensure that you select the references that have been published in the last words and go through each to check for credibility. Ensure that you obtain the references in the required format, for example, in APA, so that you can save time when creating the final reference list.
You can also group the references according to their themes that align with the outline of the paper. Go through each reference for its content and summarize the key concepts, arguments and findings for each source. You can write down your reflections on how each reference connects to the topic you are researching about. After the above steps, you can develop a strong thesis that is clear, concise and arguable. Next you should create a detailed outline of the paper so that it can help you to create headings and subheadings to be used in the paper. Ensure that you plan what point will go into each paragraph.
How to Write the Introduction for NURS 6521 Week 3 EmmaGarcia Asthma and Stepwise Management
The introduction of the paper is the most crucial part as it helps to provide the context of your work, and will determine if the reader will be interested to read through to the end. You should start with a hook, which will help capture the reader’s attention. You should contextualize the topic by offering the reader a concise overview of the topic you are writing about so that they may understand its importance. You should state what you aim to achieve with the paper. The last part of the introduction should be your thesis statement, which provides the main argument of the paper.
How to Write the Body for NURS 6521 Week 3 EmmaGarcia Asthma and Stepwise Management
The body of the paper helps you to present your arguments and evidence to support your claims. You can use headings and subheadings developed in the paper’s outline to guide you on how to organize the body. Start each paragraph with a topic sentence to help the reader know what point you will be discussing in that paragraph. Support your claims using the evidence conducted from the research, ensure that you cite each source properly using in-text citations. You should analyze the evidence presented and explain its significance and how it connects to the thesis statement. You should maintain a logical flow between each paragraph by using transition words and a flow of ideas.
How to Write the In-text Citations for NURS 6521 Week 3 EmmaGarcia Asthma and Stepwise Management
In-text citations help the reader to give credit to the authors of the references they have used in their works. All ideas that have been borrowed from references, any statistics and direct quotes must be referenced properly. The name and date of publication of the paper should be included when writing an in-text citation. For example, in APA, after stating the information, you can put an in-text citation after the end of the sentence, such as (Smith, 2021). If you are quoting directly from a source, include the page number in the citation, for example (Smith, 2021, p. 15). Remember to also include a corresponding reference list at the end of your paper that provides full details of each source cited in your text. An example paragraph highlighting the use of in-text citations is as below:
The integration of technology in nursing practice has significantly transformed patient care and improved health outcomes. According to Smith (2021), the use of electronic health records (EHRs) has streamlined communication among healthcare providers, allowing for more coordinated and efficient care delivery. Furthermore, Johnson and Brown (2020) highlight that telehealth services have expanded access to care, particularly for patients in rural areas, thereby reducing barriers to treatment.
How to Write the Conclusion for NURS 6521 Week 3 EmmaGarcia Asthma and Stepwise Management
When writing the conclusion of the paper, start by restarting your thesis, which helps remind the reader what your paper is about. Summarize the key points of the paper, by restating them. Discuss the implications of your findings and your arguments. End with a call to action that leaves a lasting impact on the reader or recommendations.
How to Format the Reference List for NURS 6521 Week 3 EmmaGarcia Asthma and Stepwise Management
The reference helps provide the reader with the complete details of the sources you cited in the paper. The reference list should start with the title “References” on a new page. It should be aligned center and bolded. The references should be organized in an ascending order alphabetically and each should have a hanging indent. If a source has no author, it should be alphabetized by the title of the work, ignoring any initial articles such as “A,” “An,” or “The.” If you have multiple works by the same author, list them in chronological order, starting with the earliest publication.
Each reference entry should include specific elements depending on the type of source. For books, include the author’s last name, first initial, publication year in parentheses, the title of the book in italics, the edition (if applicable), and the publisher’s name. For journal articles, include the author’s last name, first initial, publication year in parentheses, the title of the article (not italicized), the title of the journal in italics, the volume number in italics, the issue number in parentheses (if applicable), and the page range of the article. For online sources, include the DOI (Digital Object Identifier) or the URL at the end of the reference. An example reference list is as follows:
References
Johnson, L. M., & Brown, R. T. (2020). The role of telehealth in improving patient outcomes. Journal of Nursing Care Quality, 35(2), 123-130. https://doi.org/10.1097/NCQ.0000000000000456
Smith, J. A. (2021). The impact of technology on nursing practice. Health Press.
NURS 6521 Week 3 EmmaGarcia Asthma and Stepwise Management Sample Presentation Notes
Slide 1 – Introduction
Welcome to this staff education session on Asthma Management.
This presentation aims to provide valuable insights into understanding and effectively managing asthma in patients.
Healthcare professionals can enhance patient outcomes and the standard of care by improving their knowledge and expertise in managing asthma.
This presentation will explore key concepts, treatment options, and stepwise approaches that empower healthcare providers to deliver optimal care for patients with asthma.
Slide 2 – Long-Term Control Treatment Options for Asthma
In asthma management, various medications play vital roles in achieving long-term control of the disease. Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are the cornerstone of long-term control as they effectively reduce airway inflammation, a key component of asthma. These medications help prevent and manage asthma symptoms by reducing inflammation and improving overall lung function. Long-acting beta-agonists (LABAs) are often used in combination with ICS. They work by relaxing the airway muscles, resulting in bronchodilation and improved airflow (Rosenthal & Burchum, 2021). LABAs provide sustained relief and help control symptoms for an extended period.
Leukotriene modifiers are another class of medications used in asthma management. They block the chemicals responsible for inflammation and constriction of the airways, helping to prevent asthma symptoms. Immunomodulators are medications that modify the immune response to prevent asthma symptoms. They target specific components of the immune system involved in the inflammatory process, thereby reducing the frequency and severity of asthma attacks.
Mast cell stabilizers are used to prevent the release of asthma-triggering chemicals from mast cells (Rosenthal & Burchum, 2021). By stabilizing these cells, mast cell stabilizers help reduce airway inflammation and prevent the onset of asthma symptoms. For severe asthma cases, monoclonal antibodies are utilized. These medications target specific immune molecules involved in the inflammatory cascade of asthma. Monoclonal antibodies help control severe asthma symptoms and reduce the frequency of exacerbations, offering a targeted approach to treatment (Rosenthal & Burchum, 2021).
Slide 3 – Quick Relief Treatment Options for Asthma
Short-acting beta-agonists (SABAs) are crucial in asthma management as they provide quick relief during acute symptoms by rapidly relaxing the airway muscles and promoting bronchodilation. They are commonly used as rescue medications to alleviate sudden asthma attacks. Anticholinergics, often used in combination with SABAs, help relax the airway muscles further and improve bronchodilation (Rosenthal & Burchum, 2021). By blocking the action of acetylcholine, these medications reduce airway constriction and improve airflow.
Systemic corticosteroids play a vital role in controlling severe asthma exacerbations. These medications, typically prescribed for short periods, effectively reduce airway inflammation, improve lung function, and help manage acute episodes of asthma. Beta-agonist tablets are reserved for specific cases where immediate relief is required. They provide rapid bronchodilation and are typically used when other forms of medication or inhalers are not accessible or do not offer sufficient relief. Rescue inhalers, containing short-acting bronchodilators, offer a portable and convenient option for immediate symptom relief (Rosenthal & Burchum, 2021). They are designed to be used on the go and provide quick relief by delivering medication directly to the airways.
A personalized asthma action plan is an essential tool that empowers patients to manage their symptoms and treatment effectively. It provides clear instructions on medication usage, trigger avoidance, and steps to take during worsening symptoms or exacerbations (Rosenthal & Burchum, 2021). The asthma action plan helps patients recognize early warning signs, take appropriate actions, and maintain control over their condition.
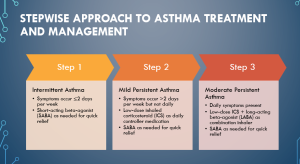
Slide 4 – Stepwise Approach to Asthma Treatment and Management
The stepwise approach to asthma treatment and management provides a structured framework for healthcare providers to tailor treatment based on the severity and frequency of symptoms experienced by patients.
Step 1 – Intermittent Asthma: At this stage, symptoms occur infrequently, with episodes happening two or fewer days per week. The recommended treatment is using a short-acting beta-agonist (SABA) as needed for quick relief. SABAs work by relaxing the airway muscles, providing immediate bronchodilation during asthma attacks. Since symptoms are sporadic, no daily controller medication is necessary at this stage (Rosenthal & Burchum, 2021).
Step 2 – Mild Persistent Asthma: In this stage, symptoms occur more frequently, happening more than two days per week, but not daily. The mainstay of treatment is a low-dose inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) as a daily controller medication. ICS reduces airway inflammation, helping to prevent symptoms and maintain asthma control. SABA is still used as needed for quick relief during exacerbations or when symptoms arise (Rosenthal & Burchum, 2021).
Step 3 – Moderate Persistent Asthma: At this stage, patients experience daily symptoms. Treatment involves a combination inhaler containing a low-dose ICS and a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA) for daily controller medication. The LABA provides additional bronchodilation and helps improve symptom control. SABA is still used as needed for quick relief during acute episodes.
Slide 5 – Asthma Treatment and Management Cont’
Step 4 – Severe Persistent Asthma: At this stage, patients experience symptoms throughout the day. The recommended treatment involves using a high-dose inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) in combination with a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA) as a daily controller medication. The combination inhaler provides potent anti-inflammatory effects and sustained bronchodilation to manage symptoms. In some cases, additional controllers like leukotriene modifiers or theophylline may be considered to further improve asthma control. SABA is still used as needed for quick relief during acute episodes (Papi et al., 2020).
Step 5 – Severe Persistent Asthma (Uncontrolled): In this stage, patients have daily symptoms and frequent exacerbations despite the use of high-dose ICS and LABA. Treatment involves a combination of high-dose ICS, LABA, and oral corticosteroids. Oral corticosteroids help to further control inflammation and manage severe symptoms. In addition, healthcare providers may consider additional therapies, such as monoclonal antibodies, which specifically target immune molecules involved in the inflammatory process of asthma. These medications are reserved for uncontrolled severe cases with standard therapies(Papi et al., 2020).
It is important to note that steps 4 and 5 of the asthma treatment plan are typically managed by asthma specialists or pulmonologists due to the complexity and severity of the condition. Regular monitoring, close follow-up, and ongoing adjustments to the treatment plan are necessary to achieve optimal asthma control and minimize the risk of complications.
Slide 6 – Stepwise Management in Asthma: Gaining and Maintaining Control
A tailored treatment approach based on individual needs, severity, and control level is essential in asthma management. Asthma is a heterogeneous condition, and patients may present with varying symptoms and levels of disease severity. By considering these factors, healthcare providers can customize treatment plans to address the specific needs of each patient (Bleecker et al., 2020). The gradual treatment intensification strategy plays a crucial role in asthma management.
Starting with the lowest effective dose of medications and then gradually increasing the treatment intensity helps minimize the risk of overtreatment and reduces the potential for side effects. This approach allows healthcare providers to find the optimal balance between symptom control and medication safety. Regular monitoring and assessment of symptoms, lung function, and exacerbation frequency are vital components of effective asthma management (Bleecker et al., 2020). By closely monitoring patients, healthcare providers can track their progress, identify any deterioration in control, and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. This proactive approach ensures timely interventions and reduces the risk of exacerbations.
Proactive prevention of exacerbations is another vital aspect of stepwise management. Treatment adjustments are made at each step to prevent and minimize the occurrence of asthma exacerbations. As patients progress through treatment, healthcare providers may modify medication dosages, add or remove specific medications, and consider additional therapies to achieve better control and prevent exacerbations. Patient empowerment and education are essential for successful asthma management. Educating patients about asthma, its triggers, and the importance of adhering to treatment plans empowers them to take an active role in their own care.
Patients can learn to recognize early warning signs of worsening asthma and promptly seek medical assistance. Empowered patients are more likely to adhere to prescribed medications, follow action plans, and engage in self-management strategies (Bleecker et al., 2020). The ultimate goal of stepwise management in asthma is achieving long-term disease control, reducing symptoms, and improving the overall quality of life for patients. With effective treatment adjustments, regular monitoring, patient education, and proactive prevention of exacerbations, healthcare providers can optimize asthma control and minimize the impact of the disease on patients’ daily lives.
References
Bleecker, E. R., Menzies-Gow, A. N., Price, D. B., Bourdin, A., Sweet, S., Martin, A. L., & Tran, T. N. (2020). Systematic literature review of systemic corticosteroid use for asthma management. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 201(3), 276-293. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201904-0903SO
Papi, A., Blasi, F., Canonica, G. W., Morandi, L., Richeldi, L., & Rossi, A. (2020). Treatment strategies for asthma: Reshaping the concept of asthma management. Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology, 16, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-020-00472-8
Rosenthal, L. D., & Burchum, J. R. (2021). Lehne’s pharmacotherapeutics for advanced practice nurses and physician assistants (2nd ed.) St. Louis, MO: Elsevier.
NURS 6521 Week 3 EmmaGarcia Asthma and Stepwise Management Instructions
INTRODUCTION
Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are significant public health burdens. Currently, more than 25 million people in the United States have asthma (HealthyPeople.gov, 2019). As an advanced practice nurse, you will likely encounter patients who will present with respiratory disorders, including asthma or COPD. Understanding specific treatment protocols as well as the types of pharmacotherapeutics used to treat respiratory disorders is important to ensure the effective and safe delivery of advanced nursing practice.
This week, you will evaluate drug therapy plans for patients who present with asthma and analyze the stepwise approach to asthma treatment and management from a patient in your professional practice.
Reference: HealthyPeople.gov. (2019). Respiratory diseases. Retrieved from https://www.healthypeople.gov/2020/topics-objectives/topic/respiratory-diseasesLinks to an external site.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Students will:
- Evaluate drug therapy plans for asthma
- Assess the impact of asthma treatments on patients
- Analyze the stepwise approach to asthma treatment and management
ASTHMA AND STEPWISE MANAGEMENT
Asthma is a respiratory disorder that affects children and adults. Advanced practice nurses often provide treatment to patients with these disorders. Sometimes patients require immediate treatment, making it essential that you recognize and distinguish minor asthma symptoms from serious, life-threatening ones. Since symptoms and attacks are often induced by a trigger, advanced practice nurses must also help patients identify their triggers and recommend appropriate management options. Like many other disorders, there are various approaches to treating and managing care for asthmatic patients depending on individual patient factors.
One method that supports the clinical decision making of drug therapy plans for asthmatic patients is the stepwise approach, which you explore in this Assignment.
To Prepare:
- Reflect on drugs used to treat asthmatic patients, including long-term control and quick relief treatment options for patients. Think about the impact these drugs might have on patients, including adults and children.
- Consider how you might apply the stepwise approach to address the health needs of a patient in your practice.
- Reflect on how stepwise management assists health care providers and patients in gaining and maintaining control of the disease.
BY DAY 7 OF WEEK 3
Create a 5- to 6-slide PowerPoint presentation that can be used in a staff development meeting on presenting different approaches for implementing the stepwise approach for asthma treatment. Be sure to address the following:
- Describe long-term control and quick relief treatment options for the asthma patient from your practice as well as the impact these drugs might have on your patient.
- Explain the stepwise approach to asthma treatment and management for your patient.
- Explain how stepwise management assists health care providers and patients in gaining and maintaining control of the disease. Be specific.
NURS 6521 Module 3: Gastrointestinal and Hepatobiliary Systems
Week 4: Gastrointestinal and Hepatobiliary Disorders
INTRODUCTION
As an advanced practice nurse, you will likely encounter patients who will present with symptoms affecting the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Of special note, is the consideration that most symptoms concerning the GI tract are non-specific and therefore, diagnosing diagnoses of the GI tract require thoughtful and careful investigation. Similarly, hepatobiliary disorders may also mirror many of the signs and symptoms that patients present when suffering from GI disorders.
How might you tease out the specific signs and symptoms between these potential disorders and body systems? What drug therapy plans will best address these disorders for your patients?
This week, you examine GI and hepatobiliary disorders. You will review a patient case study and consider those factors in recommending and prescribing a drug therapy plan for your patient.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Students will:
- Evaluate diagnoses for patients with gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary disorders
- Justify drug therapy plans based on patient history and diagnosis
PHARMACOTHERAPY FOR GASTROINTESTINAL AND HEPATOBILIARY DISORDERS
Gastrointestinal (GI) and hepatobiliary disorders affect the structure and function of the GI tract. Many of these disorders often have similar symptoms, such as abdominal pain, cramping, constipation, nausea, bloating, and fatigue. Since multiple disorders can be tied to the same symptoms, it is important for advanced practice nurses to carefully evaluate patients and prescribe a treatment that targets the cause rather than the symptom.
Once the underlying cause is identified, an appropriate drug therapy plan can be recommended based on medical history and individual patient factors. In this Assignment, you examine a case study of a patient who presents with symptoms of a possible GI/hepatobiliary disorder, and you design an appropriate drug therapy plan. Have a look at NURS 6521 Week 4 Assignment: Pharmacotherapy For Gastrointestinal And Hepatobiliary Disorders.
To Prepare:
- Review the case study assigned by your Instructor for this Assignment
- Reflect on the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and drugs currently prescribed.
- Think about a possible diagnosis for the patient. Consider whether the patient has a disorder related to the gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary system or whether the symptoms are the result of a disorder from another system or other factors, such as pregnancy, drugs, or a psychological disorder.
- Consider an appropriate drug therapy plan based on the patient’s history, diagnosis, and drugs currently prescribed.
BY DAY 7 OF WEEK 4
Write a 1-page paper that addresses the following:
- Explain your diagnosis for the patient, including your rationale for the diagnosis.
- Describe an appropriate drug therapy plan based on the patient’s history, diagnosis, and drugs currently prescribed.
- Justify why you would recommend this drug therapy plan for this patient. Be specific and provide examples.
Reminder: The College of Nursing requires that all papers submitted include a title page, introduction, summary, and references. The Sample Paper provided at the Walden Writing Center offers an example of those required elements. All papers submitted must use this formatting.
Week 4 Case Study
DC is a 46-year-old female who presents with a 24-hour history of RUQ pain. She states the pain started about 1 hour after a large dinner she had with her family. She has had nausea and on instance of vomiting before presentation.
| PMH: | Vitals: |
| HTN | Temp: 98.8oF |
| Type II DM | Wt: 202 lbs |
| Gout | Ht: 5’8” |
| DVT – Caused by oral BCPs | BP: 136/82 |
| HR: 82 bpm |
| Current Medications: | Notable Labs: |
| Lisinopril 10 mg daily | WBC: 13,000/mm3 |
| HCTZ 25 mg daily | Total bilirubin: 0.8 mg/dL |
| Allopurinol 100 mg daily | Direct bilirubin: 0.6 mg/dL |
| Multivitamin daily | Alk Phos: 100 U/L |
| AST: 45 U/L | |
| ALT: 30 U/L |
Allergies:
- Latex
- Codeine
- Amoxicillin
PE:
- Eyes: EOMI
- HENT: Normal
- GI: Nondistended, minimal tenderness
- Skin: Warm and dry
- Neuro: Alert and Oriented
- Psych: Appropriate mood
NURS 6521 Week 4: Gastrointestinal and Hepatobiliary Disorders
As an advanced practice nurse, you will likely encounter patients who will present with symptoms affecting the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Of special note, is the consideration that most symptoms concerning the GI tract are non-specific and therefore, diagnosing diagnoses of the GI tract require thoughtful and careful investigation.
Similarly, hepatobiliary disorders may also mirror many of the signs and symptoms that patients present when suffering from GI disorders.
How might you tease out the specific signs and symptoms between these potential disorders and body systems? What drug therapy plans will best address these disorders for your patients?
This week, you examine GI and hepatobiliary disorders. You will review a patient case study and consider those factors in recommending and prescribing a drug therapy plan for your patient.
Learning Objectives
Students will:
- Evaluate diagnoses for patients with gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary disorders
- Justify drug therapy plans based on patient history and diagnosis
Assignment: Pharmacotherapy for Gastrointestinal and Hepatobiliary Disorders
Photo Credit: Getty Images/iStockphoto
Gastrointestinal (GI) and hepatobiliary disorders affect the structure and function of the GI tract. Many of these disorders often have similar symptoms, such as abdominal pain, cramping, constipation, nausea, bloating, and fatigue. Since multiple disorders can be tied to the same symptoms, it is important for advanced practice nurses to carefully evaluate patients and prescribe a treatment that targets the cause rather than the symptom.
Once the underlying cause is identified, an appropriate drug therapy plan can be recommended based on medical history and individual patient factors. In this Assignment, you examine a case study of a patient who presents with symptoms of a possible GI/hepatobiliary disorder, and you design an appropriate drug therapy plan.
To Prepare
- Review the case study assigned by your Instructor for this Assignment
- Reflect on the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and drugs currently prescribed.
- Think about a possible diagnosis for the patient. Consider whether the patient has a disorder related to the gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary system or whether the symptoms are the result of a disorder from another system or other factors, such as pregnancy, drugs, or a psychological disorder.
- Consider an appropriate drug therapy plan based on the patient’s history, diagnosis, and drugs currently prescribed.
By Day 7 of Week 4
Write a 1-page paper that addresses the following:
- Explain your diagnosis for the patient, including your rationale for the diagnosis.
- Describe an appropriate drug therapy plan based on the patient’s history, diagnosis, and drugs currently prescribed.
- Justify why you would recommend this drug therapy plan for this patient. Be specific and provide examples.
Reminder: The College of Nursing requires that all papers submitted include a title page, introduction, summary, and references. The Sample Paper provided at the Walden Writing Center offers an example of those required elements. All papers submitted must use this formatting.