Informatics And Nursing Sensitive Quality Indicators NURS-FXP 4040
Informatics And Nursing Sensitive Quality Indicators NURS-FXP 4040
Nursing Informatics and the Nurse Informaticists Example
Nursing informatics is a specialty that integrates nursing and analytical and information sciences to communicate and manage data in nursing practice. It involves the application of information technology in nursing education, research, and nursing services (McGonigle & Mastrian, 2021). Therefore, nurse informaticists are nurse practitioners who incorporate information technology in nursing services to improve the quality of healthcare services.
The institutions need to use nursing informaticists to benefit from their knowledge and expertise. Furthermore, employing nursing informaticists can improve staff morale and patient outcome. Additionally, nursing informatics promotes collaboration across disciplines and professions. Besides, informatics will ensure a proper data storage system and easy follow-up of the patients.
Role of Nurse Informaticists
With the advancing technology in the world, there is a need for healthcare providers who are experts in information technology, such as nurse informaticists. According to American Informatics Association, the roles of nurse informaticists include creating protocols for data retrieval and data presentation to promote patient-centered care.
Secondly, nurse informaticists should do further studies on informatics to add new information and knowledge. Lastly, informaticists should actively promote health facility infrastructure by developing standards for communication and even advocating for evidence-based practice in the service provision (Wu et al., 2019).
Additionally, nurse informaticists should also be responsible for data validation using variety, volume, and velocity to promote a data-dependent decision-making process in the nursing practice (Garcia, 2021). The informaticists should also be in charge of implementing the new technologies in the health facility by motivating and inspiring other healthcare providers to adopt the use of technology in clinical practice.
From the above-described roles, it is apparent that the healthcare industry should promote nursing informatics expertise. This can be done by encouraging nurses to advance their studies in nursing informatics.
Nurse Informaticists and Other Health Organizations
There are several health organizations and institutions with nurse informaticists. Nurse informatics specialists can identify measures promoting transformation since they can identify existing gaps in healthcare. An example of a healthcare organization with nurse informaticists is the John Peter Smith Hospital, located in Texas.
The facility assists in recognizing red flags for domestic violence and human trafficking by applying Mobile Health and Electronic Medical records to monitor patients’ progress (Azoui et al., 2021). This method has greatly improved the nurses’ workflow and has also provided nurse practitioners with guidelines and measures for problem-solving.
Another organization of note is the Texas Hospital. The hospital has nurse informaticists who leverage technology to validate and evaluate the clinicians’ work through Electronic Medical Records. For this reason, the hospital has experienced a reduced workload from handwritten documentation to electronic health records.
The nurses in the hospital have also positively influenced the predictive model through the integration of technology and analytical strategies in clinical practice. This technique has significantly improved identifying patients who require palliation and those at high risk of mortality, hence reducing mortality rates.
Interaction Between Nurse Informaticists and other Professional Team Members
The nurse informaticists interact with the other nursing staff and the interdisciplinary team in several ways. For example, the nurse informaticists in Texas Hospital and John Peter Smith Hospital interact with staff from different disciplines by planning joint meeting sessions to equip them with technology concepts to improve healthcare outcomes.
The interdisciplinary team was enlightened on the use and advantages of adopting Electronic Medical records and Mobile Health (mHealth) (Azoui et al., 2021). Furthermore, the patients were also trained on using the tools to ease sharing and storage of data.
Impact of Nurse Engagement in Health Care Technology
The engagement of nurses in the implementation of technology tools such as the electronic medical record and mobile health has contributed a lot to improving healthcare service provision and patient outcomes. According to (Azoui et al., 2021), using mHealth has assisted in patient motivation, engagement, and behavior change. For example, healthcare workers use mHealth to monitor patient health progress through Electronic Medical Records.
In addition, the tools also enable the healthcare workers to be among themselves and with the patients. Throughout their practice, the nurse informaticists must ensure that the patients’ data recorded is per HIPAA privacy policies because the mHealth and Electronic Medical Record store confidential information about the patients. Engagement of nurses in healthcare technology has also decreased the costs of workflow.
Challenges and Opportunities
The roles of the nurse informaticists and their interaction with the interdisciplinary team have both opportunities and challenges. With nurse informaticists, health information has been easily accessible because the nurses participate in promoting healthcare technology adoption (Garcia, 2021)). For this reason, the workflow will be enhanced, making it easy to minimize errors while dealing with complex duties.
With information technology, nurses and other medical practitioners can carry out services such as drug prescription, the booking of patients, and patient monitoring by using the mHealth and Electronic Medical Record tools.
On the other hand, the challenges facing nursing informatics include difficulty in adopting technology changes but the older nurses. The older nurses during their training were not exposed to technology, and they, therefore, do not know the importance of using technology in health service provision (Luo, 2019).
The other challenge is the violation of the HIPAA privacy policies by the interdisciplinary team during the early phase of technology adoption. Additionally, the multidisciplinary team can also be influenced when an external party leaks information due to illegitimate applications.
Recommendations
This proposal has highlighted the importance of having nurse informaticists, especially for the organization that plans to adopt the healthcare technology tool to provide healthcare service. Both Texas and John Peter Smith Hospital have adopted two technology tools, the mHealth and Electronic Medical Records. Embracing technology in healthcare will enable smooth interaction between healthcare providers and patients by virtually linking up the facility services.
Based on this proposal, the following are the recommendations I would propose: First, I would advise the nurse managers and leaders to encourage the adoption and implementation of new technologies. Secondly, I would propose that the nurse administrators organize regular conferences and training to educate and train the nurses on the implementation of the latest technologies and their advantages.
I would advise the new nurses to be introduced to user-friendly technology tools to support their morale in technology adoption Informatics And Nursing Sensitive Quality Indicators NURS-FXP 4040. Lastly, I would recommend that the nurse leader organize mentorship programs to help change the nurses’ perception of the new technologies.
Informatics And Nursing Sensitive Quality Indicators NURS-FXP 4040 References
Azoui, A., Abdelouhab, K. A., & Idoughi, D. (2021, November). Design and Implementation of Cloud-Based M-Health Application for an Electronic Medical Record System. In International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Renewable Energetic Systems (pp. 458-467). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92038-8_46
Garcia-Dia, M. J. (2021). Nursing informatics: An evolving specialty. Nursing Management, 52(5), 56. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.NUMA.0000743444.08164.b4
Luo, S. (2019). Special focus issue on nursing informatics: Challenges of utilizing electronic health records. International Journal Of Nursing Sciences, 6(1), 125. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.ijnss.2018.11.001
McGonigle, D., & Mastrian, K. (2021). Nursing informatics and the foundation of knowledge. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. 128422046X, 9781284220469
Wu, D. T., Chen, A. T., Manning, J. D., Levy-Fix, G., Backonja, U., Borland, D., Caban, J. J., Dowding, D. W., Hochheiser, H., Kagan, V., Kandaswamy, S., Kumar, M., Nunez, A., Pan, E. & Gotz, D. (2019). Evaluating visual analytics for health informatics applications: a systematic review from the American Medical Informatics Association Visual Analytics Working Group Task Force on Evaluation. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 26(4), 314–323. https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocy190
Informatics And Nursing Sensitive Quality Indicators NURS-FXP 4040 Instructions
Prepare an 4-5 page paper on the importance of nursing-sensitive quality indicators.
As you begin to prepare this assessment you are encouraged to complete the Conabedian Quality Assessment Framework activity. Quality healthcare delivery requires systematic action. Completion of this will help you succeed with the assessment as you consider how the triad of structure (such as the hospital, clinic, provider qualifications/organizational characteristics) and process (such as the delivery/coordination/education/protocols/practice style or standard of care) may be modified to achieve quality outcomes.
The American Nursing Association (ANA) established the National Database of Nursing Quality Indicators (NDNQI®) in 1998 to track and report on quality indicators heavily influenced by nursing action.
NDNQI® was established as a standardized approach to evaluating nursing performance in relation to patient outcomes. It provides a database and quality measurement program to track clinical performance and to compare nursing quality measures against other hospital data at the national, regional, and state levels.
Nursing-sensitive quality indicators help establish evidence-based practice guidelines in the inpatient and outpatient settings to enhance quality care outcomes and initiate quality improvement educational programs, outreach, and protocol development.
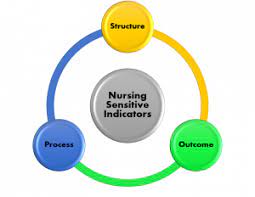
The quality indicators the NDNQI® monitors are organized into three categories: structure, process, and outcome. Theorist Avedis Donabedian first identified these categories. Donabedian’s theory of quality health care focused on the links between quality outcomes and the structures and processes of care (Grove, Gray, Jay, Jay, & Burns, 2015).
Nurses must be knowledgeable about the indicators their workplaces monitor. Some nurses deliver direct patient care that leads to a monitored outcome. Other nurses may be involved in data collection and analysis Informatics And Nursing Sensitive Quality Indicators NURS-FXP 4040. In addition, monitoring organizations, including managed care entities, exist to gather data from individual organizations to analyze overall industry quality. All of these roles are important to advance quality and safety outcomes.
The focus of Assessment 4 is on how informatics support monitoring of nursing-sensitive quality indicator data. You will develop an 8–10 minute audio (or video) training module to orient new nurses in a workplace to a single nursing-sensitive quality indicator critical to the organization. Your recording will address how data are collected and disseminated across the organization along with the nurses’ role in supporting accurate reporting and high quality results.
Reference
Grove, S. K., Gray, J. R., Jay, G.W., Jay, H. M., & Burns, N. (2015). Understanding nursing research: Building an evidence-based practice (6th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Elsevier.
Demonstration of Proficiency
By successfully completing this assessment, you will demonstrate your proficiency in the course competencies through the following assessment scoring guide criteria:
- Competency 1: Describe nurses’ and the interdisciplinary team’s role in informatics with a focus on electronic health information and patient care technology to support decision making.
- Describe the interdisciplinary team’s role in collecting and reporting quality indicator data to enhance patient safety, patient care outcomes, and organizational performance reports.
- Competency 3: Evaluate the impact of patient care technologies on desired outcomes.
- Explain how a health care organization uses nursing-sensitive quality indicators to enhance patient safety, patient care outcomes, and organizational performance reports.
- Competency 4: Recommend the use of a technology to enhance quality and safety standards for patients.
- Justify how a nursing-sensitive quality indicator establishes evidence-based practice guidelines for nurses to follow when using patient care technologies to enhance patient safety, satisfaction, and outcomes.
- Competency 5: Apply professional, scholarly communication to facilitate use of health information and patient care technologies.
- Deliver a professional and effective audio tutorial on a selected quality indicator that engages new nurses and motivates them to accurately report quality data in a timely fashion.
- Follow APA style and formatting guidelines for citations and references.
Preparation
This assessment requires you to prepare a 4-5 page paper on the importance of nursing-sensitive quality indicators. To successfully prepare for your assessment, you will need to complete the following preparatory activities:
- Select a single nursing-sensitive quality indicator that you see as important to a selected type of health care system.
- Conduct independent research on the most current information about the selected nursing-sensitive quality indicator.
- Interview a professional colleague or contact who is familiar with quality monitoring and how technology can help to collect and report quality indicator data. You do not need to submit the transcript of your conversation, but do integrate what you learned from the interview into the audio tutorial. Consider these questions for your interview:
- What is your experience with collecting data and entering it into a database?
- What challenges have you experienced?
- How does your organization share with the nursing staff and other members of the health care system the quality improvement monitoring results?
- What role do bedside nurses and other frontline staff have in entering the data? For example, do staff members enter the information into an electronic medical record for extraction? Or do they enter it into another system? How effective is this process
Informatics And Nursing Sensitive Quality Indicators NURS-FXP 4040 Instructions
For this Informatics And Nursing Sensitive Quality Indicators NURS-FXP4040 assessment, imagine you are a member of a Quality Improvement Council at any type of health care system, whether acute, ambulatory, home health, managed care, et cetera. Your Council has identified that newly hired nurses would benefit from comprehensive training on the importance of nursing-sensitive quality indicators.
The Council would like the training to address how this information is collected and disseminated across the organization. It would also like the training to describe the role nurses have in accurate reporting and high-quality results.
The Council indicates a recording is preferable to a written fact sheet due to the popularity of audio blogs. In this way, new hires can listen to the tutorial on their own time using their phone or other device.
As a result of this need, you offer to create an audio tutorial orienting new hires to these topics. You know that you will need a script to guide your audio recording. You also plan to incorporate into your script the insights you learned from conducting an interview with an authority on quality monitoring and the use of technology to collect and report quality indicator data.
You determine that you will cover the following topics in your audio tutorial script:
Introduction: Nursing-Sensitive Quality Indicator

- What is the NDNQI®?
- What are nursing-sensitive quality indicators?
- Which particular quality indicator did you select to address in your tutorial?
- Why is this quality indicator important to monitor?
- Be sure to address the impact of this indicator on quality of care and patient safety.
- Why do new nurses need to be familiar with this particular quality indicator when providing patient care?
Collection and Distribution of Quality Indicator Data
- According to your interview and other resources, how does your organization collect data on this quality indicator?
- How does the organization disseminate aggregate data?
- What role do nurses play in supporting accurate reporting and high-quality results?
- As an example, consider the importance of accurately entering data regarding nursing interventions.
Additional Requirements
- References: Cite a minimum of three scholarly and/or authoritative sources.
- APA: Submit along with the recording a separate Reference page that follows APA style and formatting guidelines. For an APA refresher, consult the APA Style and Format page on Campus.
Informatics and Nursing-Sensitive Quality Indicators Audio Script Example
Hello. I welcome you to my audio presentation on nursing and quality. My name is and I am a nurse at . In this audio presentation, I will describe nursing-sensitive quality indicators and the National Database of Nursing-Sensitive Quality Indicators. I will also describe the process of collecting and reporting quality indicator data to enhance patient safety, patient care outcomes, and organizational performance reports in our healthcare organization. You will get to understand your role in the process and why an interdisciplinary team’s input is also vital to the success of this process. Lastly, you will understand how our healthcare organization uses nursing-sensitive quality indicators.
Introduction to National Database of Nursing-Sensitive Quality Indicators
Before I describe the National Database of Nursing-Sensitive Quality Indicators, I will introduce you to what Nursing-Sensitive Quality Indicators are. A recent journal article by Afaneh et al. in 2021 defined nursing-sensitive quality indicators and reviewed recent literature on the concept of NSQIs and their implications in current practice.
Nursing-Sensitive Quality Indicators, also known as NSQIs, are a set of performance measures and outcomes that are directly or indirectly affected by nursing and thus reflect the impact of nursing care on the patients’ health. It is possible to use these indicators to establish a common ground for benchmarking and to provide evidence of the cost-effectiveness of nursing care in order to establish a benchmarking plan.
In 1988, the American Nurses Association set up a database that collected, analyzed and reported specific indicators. This database was called The National Database of Nursing Quality Indicators TM (NDNQI®). This database is headquartered at the University of Kansas Medical Center (KUMC) School of Nursing. The purpose of this database was to improve patient safety and care quality through scientific and evidence-based decision-making. Since then, there has been an increase in the use of NSQIs in healthcare as a means of measuring the impact of nursing care on patient outcomes.
In addition, it helps to identify best practices across different healthcare facilities by allowing for comparison of nursing care. Nursing leadership can also use NSQIs as a tool for allocating resources, making decisions and making decisions that improve the quality of care based on this information. These indicators include various staff measures and quality measures. NSQIs are used to evaluate the quality of nursing care and to identify areas for improvement. For this audio presentation, I selected pressure ulcer incidence rates as the NSQI.
Pressure ulcers are localized areas of damage to the skin caused by unrelieved pressure on an area of the body. Pressure ulcer incidence rates represent the latest number of cases of patients with pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores, in some care settings. Knowing the new number of cases of bedsores is crucial because it reflects the quality of nursing care that patients receive in our healthcare organization. According to the Agency for Health Care Research and Quality website, the United States has more than 2.5 million pressure ulcers each year. These skin lesions cause pain, infection, and increased healthcare use.
Therefore, this indicator is vital in improving the quality and safety of the nursing care that patients receive in the hospital. New nurses need to be familiar with this particular quality indicator when providing patient care. This is important because every admitted patient is at risk of developing pressure sores and ulcers when under your care, and it is your ethical and professional responsibility to protect your patients from preventable harm.
Collection and Distribution of Quality Indicator Data
Data on NSQIs is collected using a variety of methods, such as electronic medical records, patient surveys, and direct observation of the patient. This data is analyzed, and the results are used to identify improvements to be made, as well as to track the progress of the patient over time. I had an interview with the nurse informaticist, who is our institution’s NDNQI site coordinator. The site coordinator periodically consolidates and reports the NSQI data to the NDNQI databases and disseminates this feedback to the hospital and various institutions.
Therefore, nurse leaders and hospital administrators can use this data to make administrative decisions and policies, while direct clinical care providers can improve their care standards using these reports. Data on the incidence rates of pressure ulcers are collected through our electronic health record system, which detects entry of pressure ulcers from nurses, doctors, and other healthcare providers in the hospital, such as physician assistants. Therefore, it is important to enter accurate data when building health histories for patients.
Nurses play an important role in documenting patient data while collecting and reporting quality health indicators. Your participation in quality improvement begins with documentation of the new cases of pressure ulcers in the patient’s electronic medical record. To improve patient safety and quality regarding this particular indicator, it would be helpful to have accurate reporting to implement evidence-based quality improvement initiatives.
This also calls for interdisciplinary team input because the prevention of pressure sores requires multidisciplinary approaches. Nurses will need to collaborate with doctors and other healthcare providers to implement and evaluate various strategies based on the latest evidence to improve patients’ health. According to Sullivan et al. (2023), a number of nursing specialties and general nursing practices are represented by established NSIs.
Overall, the pressure ulcer incidence rate is just one of the many indicators that nurses need to participate in reporting and evaluating to provide safe care. As your patient’s advocate, it is your ethical call to ensure they get safe care. Therefore, a good nurse will participate in assessing, evaluating, and applying nursing-sensitive quality indicators. Thank you for listening. Until next time, Goodbye!
Informatics And Nursing Sensitive Quality Indicators NURS-FXP 4040 References
Afaneh, T., Abu-Moghli, F., & Ahmad, M. (2021). Nursing-sensitive indicators: a concept analysis. Nursing Management (Harrow, London, England: 1994), 28(3), 28–33. https://doi.org/10.7748/nm.2021.e1982
Agency for Health Care Research and Quality. (n.d.). Preventing Pressure Ulcers in Hospitals. Ahrq.gov. Retrieved January 29, 2023, from https://www.ahrq.gov/patient-safety/settings/hospital/resource/pressureulcer/tool/index.html
Sullivan, C. E., Day, S. W., Ivankova, N., Markaki, A., Patrician, P. A., & Landier, W. (2023). Establishing nursing-sensitive quality indicators for pediatric oncology: An international mixed methods Delphi study. Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 55(1), 388–400. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnu.12798
