Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051
Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051 – Step-by-Step Guide
The first step before starting to write the Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051, it is essential to understand the requirements of the assignment. The first step is to read the assignment prompt carefully to identify the topic, the length and format requirements. You should go through the rubric provided so that you can understand what is needed to score the maximum points for each part of the assignment.
It is also important to identify the audience of the paper and its purpose so that it can help you determine the tone and style to use throughout. You can then create a timeline to help you complete each stage of the paper, such as conducting research, writing the paper, and revising it to avoid last-minute stress before the deadline. After identifying the formatting style to be applied to the paper, such as APA, you should review its use, such as writing citations and referencing the resources used. You should also review how to format the title page and the headings in the paper.
How to Research and Prepare for Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051
The next step in preparing for your paper is to conduct research and identify the best sources to use to support your arguments. Identify the list of keywords from your topic using different combinations. The first step is to visit the university library and search through its database using the important keywords related to your topic. You can also find books, peer-reviewed articles, and credible sources for your topic from PubMed, JSTOR, ScienceDirect, SpringerLink, and Google Scholar. Ensure that you select the references that have been published in the last words and go through each to check for credibility. Ensure that you obtain the references in the required format, for example, in APA, so that you can save time when creating the final reference list.
You can also group the references according to their themes that align with the outline of the paper. Go through each reference for its content and summarize the key concepts, arguments and findings for each source. You can write down your reflections on how each reference connects to the topic you are researching about. After the above steps, you can develop a strong thesis that is clear, concise and arguable. Next you should create a detailed outline of the paper so that it can help you to create headings and subheadings to be used in the paper. Ensure that you plan what point will go into each paragraph.
How to Write the Introduction for Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051
The introduction of the paper is the most crucial part as it helps to provide the context of your work, and will determine if the reader will be interested to read through to the end. You should start with a hook, which will help capture the reader’s attention. You should contextualize the topic by offering the reader a concise overview of the topic you are writing about so that they may understand its importance. You should state what you aim to achieve with the paper. The last part of the introduction should be your thesis statement, which provides the main argument of the paper.
How to Write the Body for Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051
The body of the paper helps you to present your arguments and evidence to support your claims. You can use headings and subheadings developed in the paper’s outline to guide you on how to organize the body. Start each paragraph with a topic sentence to help the reader know what point you will be discussing in that paragraph. Support your claims using the evidence conducted from the research, ensure that you cite each source properly using in-text citations. You should analyze the evidence presented and explain its significance and how it connects to the thesis statement. You should maintain a logical flow between each paragraph by using transition words and a flow of ideas.
How to Write the In-text Citations for Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051
In-text citations help the reader to give credit to the authors of the references they have used in their works. All ideas that have been borrowed from references, any statistics and direct quotes must be referenced properly. The name and date of publication of the paper should be included when writing an in-text citation. For example, in APA, after stating the information, you can put an in-text citation after the end of the sentence, such as (Smith, 2021). If you are quoting directly from a source, include the page number in the citation, for example (Smith, 2021, p. 15). Remember to also include a corresponding reference list at the end of your paper that provides full details of each source cited in your text. An example paragraph highlighting the use of in-text citations is as below:
The integration of technology in nursing practice has significantly transformed patient care and improved health outcomes. According to Smith (2021), the use of electronic health records (EHRs) has streamlined communication among healthcare providers, allowing for more coordinated and efficient care delivery. Furthermore, Johnson and Brown (2020) highlight that telehealth services have expanded access to care, particularly for patients in rural areas, thereby reducing barriers to treatment.
How to Write the Conclusion for Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051
When writing the conclusion of the paper, start by restarting your thesis, which helps remind the reader what your paper is about. Summarize the key points of the paper, by restating them. Discuss the implications of your findings and your arguments. End with a call to action that leaves a lasting impact on the reader or recommendations.
How to Format the Reference List for Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051
The reference helps provide the reader with the complete details of the sources you cited in the paper. The reference list should start with the title “References” on a new page. It should be aligned center and bolded, in sentence sentence care. The references should be organized in an ascending order alphabetically and each should have a hanging indent. If a source has no author, it should be alphabetized by the title of the work, ignoring any initial articles such as “A,” “An,” or “The.” If you have multiple works by the same author, list them in chronological order, starting with the earliest publication.
Each reference entry should include specific elements depending on the type of source. For books, include the author’s last name, first initial, publication year in parentheses, the title of the book in italics, the edition (if applicable), and the publisher’s name. For journal articles, include the author’s last name, first initial, publication year in parentheses, the title of the article (not italicized), the title of the journal in italics, the volume number in italics, the issue number in parentheses (if applicable), and the page range of the article. For online sources, include the DOI (Digital Object Identifier) or the URL at the end of the reference. An example reference list is as follows:
References
Johnson, L. M., & Brown, R. T. (2020). The role of telehealth in improving patient outcomes. Journal of Nursing Care Quality, 35(2), 123-130. https://doi.org/10.1097/NCQ.0000000000000456
Smith, J. A. (2021). The impact of technology on nursing practice. Health Press.
Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051 Example 1
The Concept of a Knowledge Worker
- Employs intellect to analyze, create, and share valuable information.
- Utilizes expertise to solve complex problems and make informed decisions.
- Relies on continuous learning and innovation for professional growth.
- Leverages technology to access, organize, and disseminate knowledge effectively.
- Collaborates with multidisciplinary teams to improve patient outcomes and care.
- Drives evidence-based practices and fosters a culture of lifelong learning.
Nursing Informatics – Definition and Explanation
- Integration of nursing science, computer science, and information science.
- Enhances healthcare through data management, knowledge dissemination, and technology.
- Improves patient care, safety, and outcomes through evidence-based practice.
- Utilizes technology to collect, analyze, and interpret healthcare data.
- Supports decision-making, research, and quality improvement in nursing practice.
- Optimizes information systems to streamline workflows and enhance communication
- (Kianto et al., 2019)
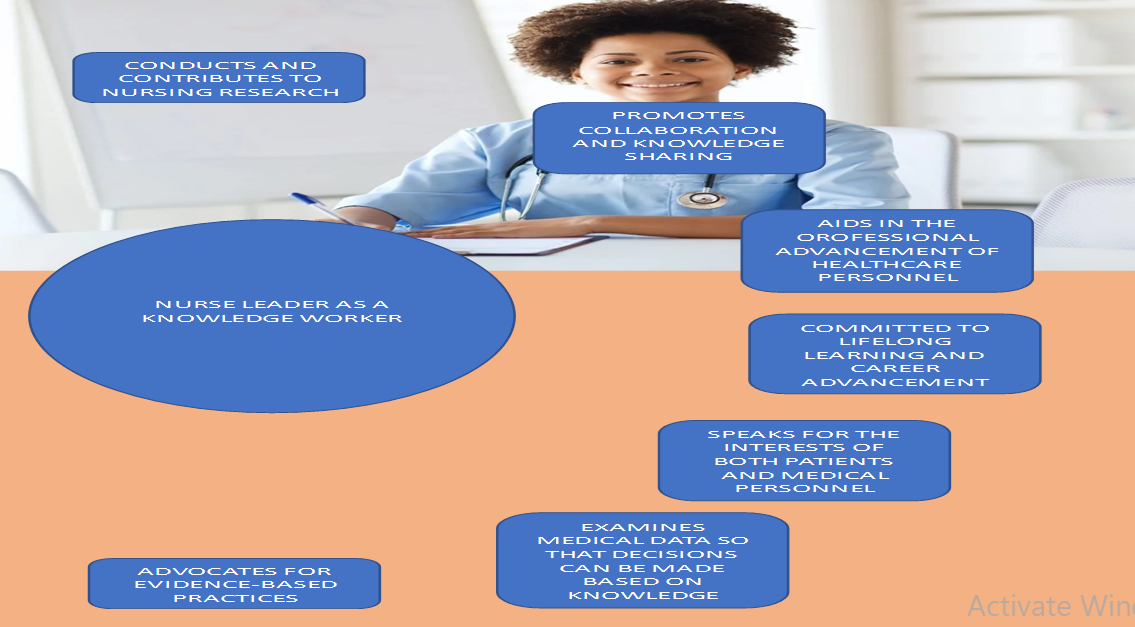
Nurse Leader as a Knowledge Worker
- Strategically integrates evidence-based practices into nursing leadership.
- Promotes continuous learning and professional development among the team.
- Facilitates knowledge sharing and collaboration across healthcare disciplines.
- Utilizes data and technology to drive informed decision-making and innovation.
- Advocates for a culture of lifelong learning and evidence-based care.
- Inspires and empowers the team to embrace knowledge-driven practices.
- (Strudwick et al., 2019)
The Application of Data to Problem-Solving in Healthcare
- Examining data: Vital signs, glucose levels, physical activity, sleep patterns.
- Data collection: Wearable devices, sensors, secure transmission to a centralized database.
- Derived knowledge: Early identification, personalized treatment, proactive preventive care.
- Accessing data: Secure web portal, a mobile application for real-time monitoring.
- Clinical reasoning: Nurse leaders interpret data, consider patient context.
- Improving outcomes: Data-driven insights, evidence-based practice, process improvement.
The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051 References
Garcia-Dia, M. J. (2021). Nursing informatics: an evolving specialty. Nursing Management, 52(5), 56. https://journals.lww.com/nursingmanagement/fulltext/2021/05000/nursing_informatics__an_evolving_specialty.10.aspx
Kianto, A., Shujahat, M., Hussain, S., Nawaz, F., & Ali, M. (2019). The impact of knowledge management on knowledge worker productivity. Baltic Journal of Management, 14(2), 178-197. https://hub.hku.hk/bitstream/10722/278661/1/Content.pdf?accept=1
Strudwick, G., Nagle, L., Kassam, I., Pahwa, M., & Sequeira, L. (2019). Informatics Competencies for Nurse Leaders: A Scoping Review. The Journal of Nursing Administration, 49(6), 323–330. https://doi.org/10.1097/NNA.0000000000000760
Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051 / NURS 5051 Instructions
Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker
The term “knowledge worker” was first coined by management consultant and author Peter Drucker in his book, The Landmarks of Tomorrow (1959). Drucker defined knowledge workers as high-level workers who apply theoretical and analytical knowledge, acquired through formal training, to develop products and services. Does this sound familiar?
Nurses are very much knowledge workers. What has changed since Drucker’s time are the ways that knowledge can be acquired. The volume of data that can now be generated and the tools used to access this data have evolved significantly in recent years and helped healthcare professionals (among many others) to assume the role of knowledge worker in new and powerful ways.
In this Assignment, you will consider the evolving role of the nurse leader and how this evolution has led nurse leaders to assume the role of knowledge worker. You will prepare a PowerPoint presentation with an infographic (graphic that visually represents information, data, or knowledge. Infographics are intended to present information quickly and clearly.) to educate others on the role of nurse as knowledge worker. Have a look at Discussion: Interaction Between Nurse Informaticists and Other Specialists NURS 6051.
Reference: Drucker, P. (1959). The landmarks of tomorrow. New York, NY: HarperCollins Publishers.
To Prepare for this The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051:
- Review the concepts of informatics as presented in the Resources.
- Reflect on the role of a nurse leader as a knowledge worker.
- Consider how knowledge may be informed by data that is collected/accessed.
The Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051:
- Explain the concept of a knowledge worker.
- Define and explain nursing informatics and highlight the role of a nurse leader as a knowledge worker.
- Include one slide that visually represents the role of a nurse leader as knowledge worker.
- Your PowerPoint should Include the hypothetical scenario you originally shared in the Discussion Forum. Include your examination of the data that you could use, how the data might be accessed/collected, and what knowledge might be derived from that data. Be sure to incorporate feedback received from your colleagues’ responses.
By Day 7 of Week 2
Submit your completed Presentation.
Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051 Example 2 Presentation
The Knowledge Worker
- Knowledge workers are people who use their theoretical knowledge and acquired skills through formal training to deliver productive work (Druker, 1995).
- Knowledge workers use their knowledge and skills to solve complex problems, make decisions, and provide new services.
- Knowledge workers access and synthesize information and use analytic reasoning and relevant judgments in addressing issues and new situations.
- Good communication skills and adequate motivation help knowledge workers deliver quality service.
- A professional board always governs knowledge workers
- Knowledge workers receive higher compensation due to the complex nature of their work
Nursing Informatics
- Nursing informatics combines nursing science, information science, and computer science (McGonigle & Mastrian, 2015.)
- This combination helps identify, define, manage, and communicate information, wisdom, and data in nursing practice to improve patient care.
- Nursing informatics includes bed management systems that help manage patient census and an electronic portal that allows patients to access their medical records quickly.
- Radio frequency identification is another example of nursing informatics that aids in tracking patient and caregiver activities.
- Nursing informatics is essential in increasing patient safety and promoting quality healthcare in hospital settings.
- Nursing informatics plays a vital role in training nursing staff on the use of technology, answering questions, and monitoring results.
Nursing informatics improve patient care by:
- Designing different process of treatment approaches, reviewing clinical workflow, diagnostic and treatment plans
- Measuring and analyzing different parts of organizational roles and making specific changes that help in improving patient care.
- Analyzing several data information to identify prevalent issues in healthcare organizations and provide the best solutions
- Selecting and testing new medical devices used in improving patient care.
- Providing training to other nursing staff by providing educational programs.
- Implementing information systems provides better access to evidence affecting patient safety and supports evidence-based nursing.
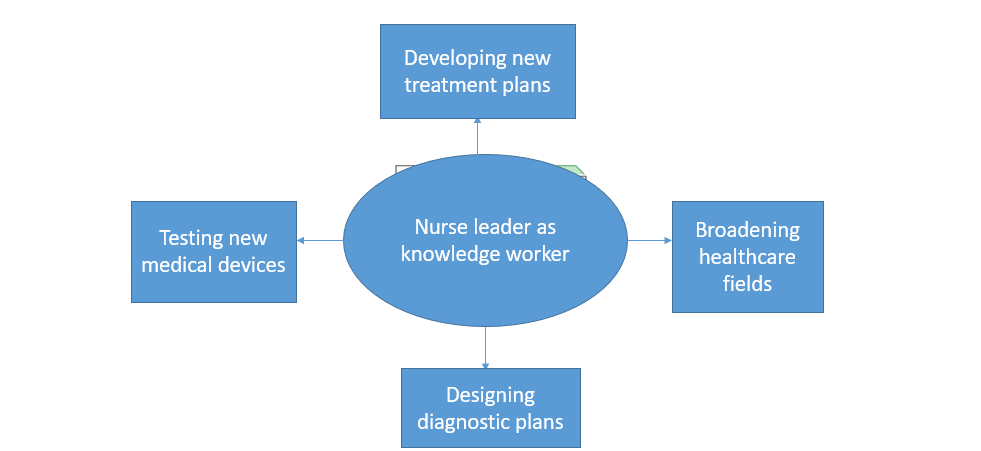
Role of a Nurse as a Knowledge Worker
- Nurse leaders play a crucial work in developing new treatment plans, collecting and evaluating treatment plans
- Using their autonomy and nursing experience, nursing leaders aid in broadening healthcare fields and promoting health
- Nurse leaders apply their knowledge and skills to address the needs of their patients and level up the general patient care criteria.
- Nurse leaders use their acquired integrated knowledge to solve upcoming and existing practice problems in healthcare settings.
- Nurse leaders are equipped with informatics skills that aid in developing new research on different nursing practices that help in improving outcomes of patient needs.
The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051 Presentation References
- Drucker, P. (1959). Landmarks of Tomorrow: A Report on the New” Post-Modern. World.
- McGonigle, D., & Mastrian, K. G. (Eds.). (2015). Nursing informatics and the foundation of knowledge. Jones & Bartlett Publishers
NURS 6051 Week 3 Discussion: Interaction Between Nurse Informaticists and Other Specialists
Nature offers many examples of specialization and collaboration. Ant colonies and bee hives are but two examples of nature’s sophisticated organizations. Each thrives because their members specialize by tasks, divide labor, and collaborate to ensure food, safety, and general well-being of the colony or hive.
Of course, humans don’t fare too badly in this regard either. And healthcare is a great example. As specialists in the collection, access, and application of data, nurse informaticists collaborate with specialists on a regular basis to ensure that appropriate data is available to make decisions and take actions to ensure the general well-being of patients.
In this Discussion, you will reflect on your own observations of and/or experiences with informaticist collaboration. You will also propose strategies for how these collaborative experiences might be improved.
To Prepare:
- Review the Resources and reflect on the evolution of nursing informatics from a science to a nursing specialty.
- Consider your experiences with nurse Informaticists or technology specialists within your healthcare organization.
By Day 3 of Week 3
Post a description of experiences or observations about how nurse informaticists and/or data or technology specialists interact with other professionals within your healthcare organization. Suggest at least one strategy on how these interactions might be improved. Be specific and provide examples. Then, explain the impact you believe the continued evolution of nursing informatics as a specialty and/or the continued emergence of new technologies might have on professional interactions.
By Day 6 of Week 3
Respond to at least two of your colleagues* on two different days, offering one or more additional interaction strategies in support of the examples/observations shared or by offering further insight to the thoughts shared about the future of these interactions.
*Note: Throughout this program, your fellow students are referred to as colleagues.
